Orthopaedic electrical stimulation devices have emerged as a revolutionary innovation in the field of rehabilitation and recovery. These sophisticated devices employ electrical signals to enhance the healing process of bones and soft tissues, making them an invaluable tool in orthopaedic medicine. By delivering controlled electrical impulses to targeted areas, they promote cellular activity, reduce inflammation, and facilitate tissue repair, thereby aiding patients in their recovery journey.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in understanding how these devices function and their diverse applications in clinical settings. The mechanisms behind orthopaedic electrical stimulation devices are rooted in the principles of bioelectricity, drawing on the body’s natural processes to improve healing outcomes. This article delves into the functionality of these innovative devices, exploring their benefits and potential for enhancing the recovery experience post-injury or surgery.
As we navigate through the complexities of modern orthopaedics, it is crucial to grasp the significance of orthopaedic electrical stimulation devices. They represent a convergence of technology and medicine that promises to redefine therapeutic approaches and improve patient outcomes, fostering a new era in the management of musculoskeletal injuries and disorders.
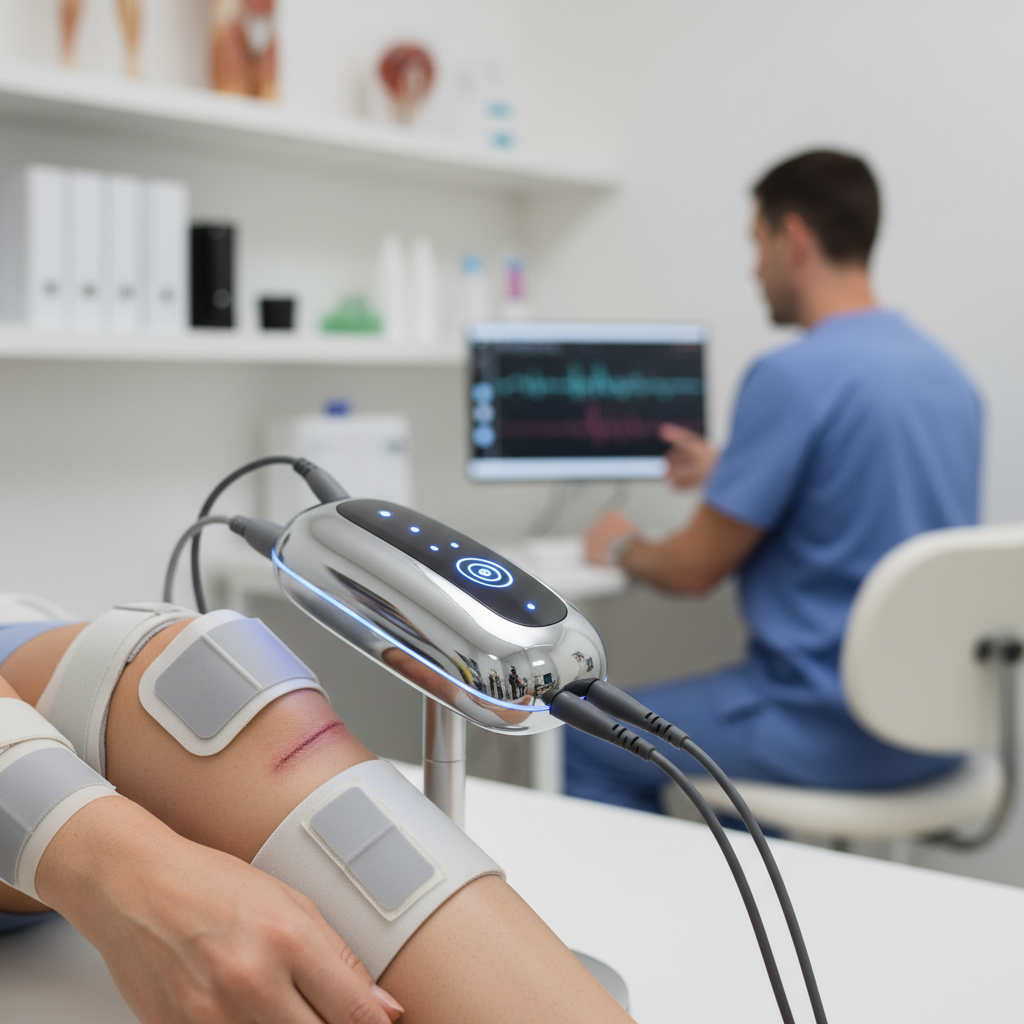
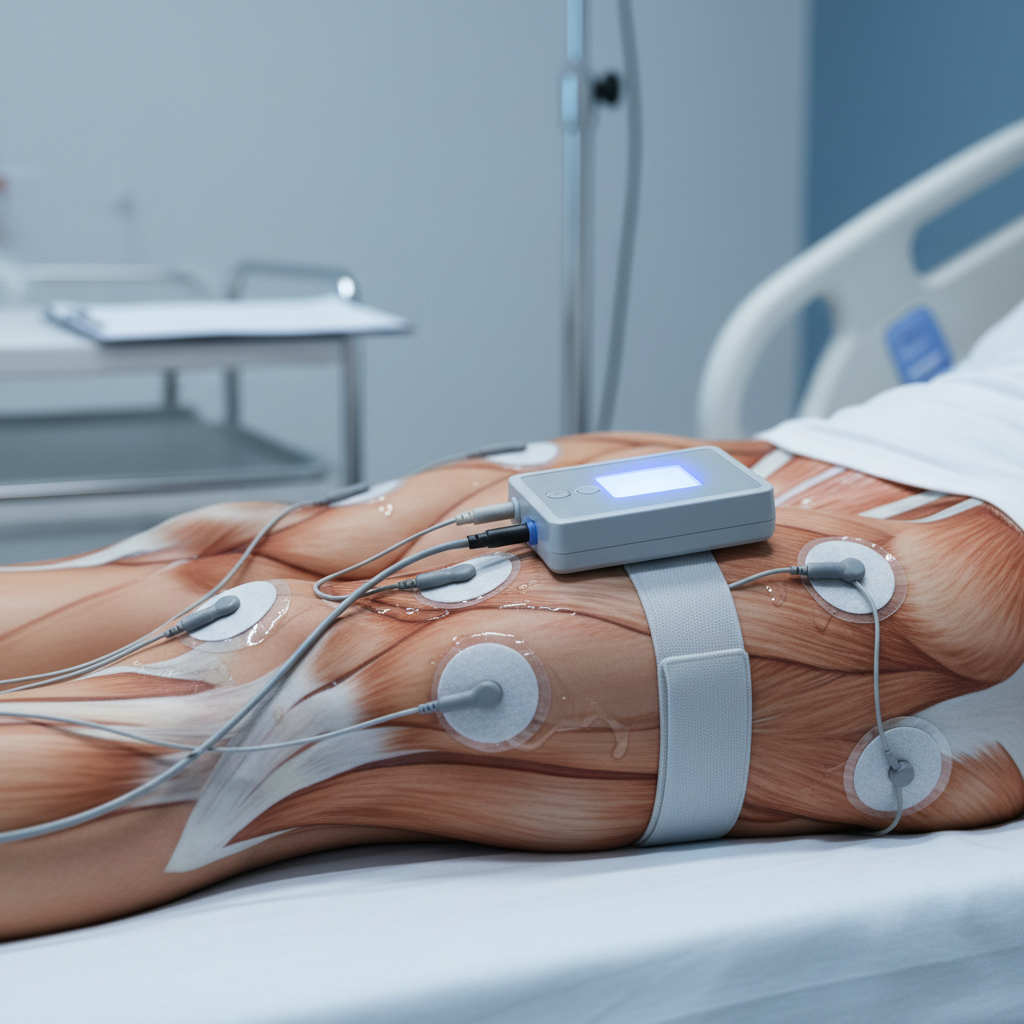
Orthopaedic electrical stimulation devices are becoming increasingly vital in muscle recovery and enhancement. These devices primarily use electrical impulses to stimulate muscles and promote healing in soft tissues and bones. Recent studies indicate that neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) can significantly increase femoral venous blood flow following total hip prosthesis procedures, supporting postoperative recovery. Such stimulation mechanisms have reported promising outcomes, suggesting their efficacy in accelerating muscle strength and enhancing recovery across various patient profiles.
The market for these devices is expanding dramatically, with projections forecasting the trauma and extremities devices sector to reach USD 24.90 billion by 2034. Innovations in technologies, such as capacitive electrode systems, allow for personalized electric stimuli delivery, targeting specific tissues for optimized recovery. This progress enhances treatment modalities in orthopaedics, showing potential in applications ranging from preventing deep vein thrombosis post-surgery to improving gait in populations with neuromuscular deficits. The continuous advancement in electrical stimulation technologies marks a significant stride in enhancing orthopaedic care and rehabilitation outcomes.
Electrical stimulation in orthopaedics is a therapeutic approach that harnesses electrical signals to promote healing and regeneration in musculoskeletal tissues. The underlying principle is based on the body’s natural cellular responses to electrical fields, which can enhance tissue repair processes. When the device is applied to the affected area, it generates pulses that stimulate nerve and muscle fibers, encouraging blood flow and delivering essential nutrients to the site of injury. This process can significantly reduce recovery times and improve functional outcomes in patients with fractures, tendinitis, or post-surgical rehabilitation.
**Tips:** If you’re considering an orthopaedic electrical stimulation device, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate type and duration of use tailored to your specific condition. Maintaining consistent follow-up appointments will help monitor progress and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
In addition to direct stimulation, these devices can also help alleviate pain. By modulating pain signals before they reach the brain, electrical stimulation provides a non-invasive alternative to medication. The effectiveness may vary, so keeping a journal of your pain levels and responses can offer valuable insights into what works best for your situation.
**Tips:** Always ensure the device is used as prescribed and monitor for any adverse reactions. Staying informed about technological advancements and ongoing studies can provide additional options for your recovery journey.
Orthopaedic electrical stimulation devices are increasingly utilized in rehabilitation to facilitate healing in musculoskeletal injuries. There are several types of these devices, each tailored for specific applications. The most common types include transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), microcurrent stimulation (MCS), and pulsed electromagnetic field therapy (PEMF). TENS is primarily used for pain management; it sends electrical impulses through the skin to disrupt pain signals. Microcurrent stimulation promotes cellular repair and regeneration, often used in the recovery phase post-surgery or injury.
Pulsed electromagnetic field therapy, on the other hand, uses electromagnetic fields to improve blood circulation and reduce inflammation, making it a good choice for chronic conditions or post-operative recovery. Each device not only targets unique aspects of healing but also supports physical therapy efforts by enhancing muscle function and alleviating pain. The choice of device often depends on the patient's specific condition, recovery goals, and the healthcare provider’s recommendation, ensuring that treatment is both effective and tailored to individual needs.
| Type of Device | Main Application | Mechanism of Action | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) | Pain Relief | Uses electrical impulses to stimulate nerves | Non-invasive pain management, minimal side effects |
| Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS) | Muscle Rehabilitation | Contracts muscles through electrical impulses | Improves muscle strength and recovery |
| Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) | Assists Movement | Stimulates muscular contraction for movement | Enhances mobility and improves quality of life |
| Bone Growth Stimulator | Fracture Healing | Promotes bone growth through electrical stimulation | Accelerates healing of fractures |
| Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES) | Muscle Recovery | Stimulates muscles to restore function | Reduces muscle atrophy during rehabilitation |
Electrical stimulation (ES) is emerging as a powerful tool in promoting healing, particularly in the context of chronic wound care and nerve regeneration. Research has shown that the application of electrical currents enhances the healing process by modulating cellular behavior. A recent review emphasized the synergistic effects of ES combined with adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) in wound healing, where electrical stimulation activates cellular pathways that promote tissue regeneration. This approach not only accelerates healing but may also reduce the risk of infections by enhancing the immune response at the injury site.
Further advancements highlight the ability of electrical stimulation to reprogram immune cells, such as macrophages, to reduce inflammation and facilitate faster recovery. Studies from Trinity College Dublin illustrate how targeted electrical impulses can lead to favorable alterations in the immune environment, subsequently leading to improved healing outcomes.
Moreover, the innovative use of bioscaffolds with electrical stimulation is being explored to enhance peripheral nerve regeneration, addressing the significant challenges posed by peripheral nerve injuries that often result in long-term dysfunction. As the field continues to evolve, these mechanisms of action underscore the promising role of electrical stimulation in modern therapeutic strategies for diverse injuries and conditions.
The field of orthopaedic electrical stimulation technology is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in materials, design, and our understanding of cellular responses to electrical signals. Future trends indicate a move towards more personalized treatment options, integrating wearable technology that can monitor and adapt stimulation based on patient-specific data. This personalization could enhance recovery times and overall effectiveness, making it a promising avenue for future research and development.
As innovations continue, the incorporation of smart technology into orthopaedic devices will likely gain traction. Devices could feature real-time feedback mechanisms, allowing healthcare providers to adjust parameters remotely for optimal patient outcomes. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence might enhance the predictive analytics of treatment plans, leading to even more precise and effective interventions.
**Tips:** When considering orthopaedic electrical stimulation devices, always consult your healthcare provider to understand the best options tailored to your needs. Additionally, staying informed about new technologies can help you take advantage of the latest advancements that may benefit your recovery process. Emphasizing adherence to the prescribed treatment plan will also maximize the effectiveness of these innovative devices.





*The content on this website is for general informational purposes only and should not be taken as medical advice. Please contact your physician or therapist to learn what therapy solution is suitable for your specific needs. Not all products, features, or indications shown are approved in all countries.